Notice of Site Closure
Thank you very much for using Panasonic Kids School.
This website will be discontinued as of March 31, 2026.We sincerely appreciate your support and loyalty over the years.

-
When and how was the Earth formed?
-
What other things are like the Earth?
-
Is it true the Earth didn’t have oceans at the very beginning?
-
How come is the Earth called the Water Planet?
-
How was the Earth’s land made?
-
Is it true the continents are moving?
-
Is the Earth still active?
-
What’s the center of the Earth like?
-
Is the Earth moving really fast?
-
Why does the Earth’s temperature change?
-
Why doesn’t the Earth run out of water?
-
What will happen to the Earth at the very end?
-
Is it true people in ancient times didn’t know the Earth is round?
When and how was the Earth formed?
When and how was our home, the Earth, formed? The Earth is located in a vast universe. The Earth is in a solar system at the edge of a cluster of stars called the Milky Way galaxy. Now, let’s look into the secret of the Earth’s formation.
The events that started the Earth’s formation go back about 5 billion years ago. Somewhere in the universe, a star exploded. The force of the blast created a large swirling of fine gas and dust particles. Matter gathered together at the center of the swirl and got hotter and hotter. Eventually, the matter got hot enough to trigger a nuclear fusion reaction. What this produced is the sun.
At the same time, gases in the circling swirl cooled and formed tiny particles. These particles grouped together and eventually formed large masses called minor planets. The minor planets were drawn together by gravitational attraction, making bigger and bigger minor planets. These were the original forms of the Earth and other planets. The original Earth is thought to have formed about 4.6 billion years ago.
What other things are like the Earth?
Did you know the Earth was formed from a swirl of tiny gas and dust particles? Around the same time, gases and dust clumped together to make other planets.
There are eight planets in our solar system. Starting from the closest to the sun, they are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. You can think of the solar system’s planets as brothers and sisters. Even though the planets are in the same solar system, they are different sizes and have different characteristics. The four planets closest to the sun — Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars — are smaller and are made of rock. Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus are mostly made of gas and are very large.

The Earth has lots of air and water and is home to a rich diversity of life forms. You can say the Earth is a very special planet with lots of characteristics not found on any other planet in the solar system.
Is it true the Earth didn’t have oceans at the very beginning?
Can you imagine what the Earth looked like immediately after it was formed? At the very beginning, the Earth didn’t have any oceans or any land. The Earth was a huge sea of hot magma. Magma is rock that has melted at temperatures over 1,200 degrees Celsius. Many minor planets and meteorites were also crashing into the Earth at this time. High in the sky, water vapor started to gather and make clouds.
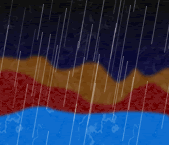
Eventually, as fewer minor planets and meteorites hit the Earth, the sea of magma began to cool. When the Earth’s surface temperature fell to around 300 degrees Celsius, clouds formed near the surface and rain started to fall. The rain cooled the hot surface very quickly.
And as the surface cooled more, the water vapor in the atmosphere also cooled, causing more rain. The rainwater pooled on the Earth’s surface, making rivers, ponds, and lakes. Huge floods happened over and over again. The floods joined the pools of water together until they eventually turned into oceans. It poured rain constantly for an incredible 3,000 years. By the way, do you know why the oceans are salty?
How come is the Earth called the Water Planet?
From space, the Earth looks like a blue shining planet. This is because 70 percent of the Earth’s surface is covered by water. And this is why the Earth is called the Water Planet.

As the oceans formed on the Earth, it has been the only planet in our solar system that hosts a rich diversity of life forms. Although not all the details are known yet, it’s believed the first life forms emerged in the oceans. The combination of things like oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen dissolved in seawater created the first living cells. So life, the ancestor of all living things on the planet, originated in the oceans.
The oceans not only created life; they also helped protect life. Life on Earth first originated about 4 billion years ago. Living things faced many dangers on land at that time. For example, the sun’s ultraviolet rays were several times stronger than they are today. This is why life forms continued to evolve in the oceans for many millions of years. This is where the expression Mother Sea comes from.
How was the Earth’s land made?
Right after the Earth was formed, it was covered by a sea of hot magma. Once oceans eventually formed, the Earth was almost completely covered by oceans. If you looked at just the surface, you would think the Earth was a ball of water.
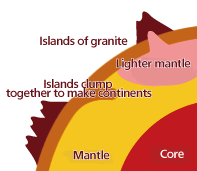
But how was land made if everything was covered by water? Let's take a look at the bottom of the oceans and the inside of the Earth. The ocean floor was covered by the Earth’s crust. The crust is made up of a thin layer of rock. Under the crust was a hot mass of rock called the mantle.
Several hundred million years after the Earth was formed, an even hotter core formed in the center of the Earth. The super-hot core heated the mantle, which made the mantle lighter and caused it to rise up. This mantle was cooled at the ocean floor and became plates, or bedrock. These plates moved with the flow of the mantle and collided with other plates. At the boundaries where plates collided, lots of islands were formed. The islands were made of a light rock called granite. It’s thought these granite islands collided and clumped together, eventually creating continents.
Is it true the continents are moving?
Take a good look at a world map or a globe. If you moved North and South America and placed them beside Africa, can you see how neatly they would line up? About 220 million years ago, all of today’s continents were joined together in one super huge continent. It’s believed cracks formed in the super continent and the pieces slowly drifted apart. Over time, these pieces moved into their current shape.
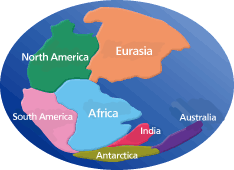
So why did the continents move? The answer is related to the mantle inside the Earth. The mantle is a hot mass of rock that moves under the Earth’s surface. The mantle’s movement causes the continents to move.
For example, the area where the Himalayas are now was once a shallow sea long ago. What happened was the Indian subcontinent drifted and collided with Asia. The powerful impact raised the sea up into the sky and formed the Himalayas. The Japanese archipelago was sunk at the bottom of the sea until about 300 million years ago. The archipelago rose up from the seafloor about 200 million years ago, rising above the sea and sinking back down again and again. All this time, it was joined to the Asian continent. The continent and Japan were connected by land until about 100,000 years ago. People, animals, and other living things were able to come to Japan because of the land bridge.
Is the Earth still active?
The Earth has been constantly active since it was formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Even today, volcanic eruptions and changes in the Earth’s crust still affect the oceans and continents in many ways.

Volcanic eruptions occur when rock melts into magma. The magma breaks through the Earth’s surface and spews out. Volcanic eruptions can cause major disasters from hot lava flowing out of the volcano and from volcanic ash and steam spewed up in the air. Did you know volcanic eruptions can even make new mountains?
Another sign the Earth is active are earthquakes, which cause the ground to shake and move. People do not know exactly why earthquakes happen. We do know earthquakes are caused by movements of the crust and plates in rock formations along fault lines. When rock formations crack after resisting very big pressures, the shocks are sent through the ground causing the ground to shake. The Earth truly is like a living being.
What’s the center of the Earth like?
What exactly is the center of the Earth like? The inside of the Earth is a bit like a half-boiled egg. The Earth’s surface is covered by a very thin layer called the crust. We dig into the crust to obtain minerals and fuels like coal and oil. But looking at the entire planet, this layer is like a very thin shell of an egg.
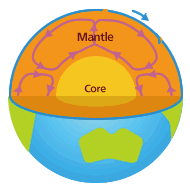
If we go down deeper toward the center of the Earth, we will reach a layer called the mantle. The mantle is like the white part of an egg. Going farther down beyond the mantle, we will reach the core, which is like the yolk of an egg. The core is molten and is said to be as hot as 6,000 degrees Celsius. The mantle is made of rock. When rock in the mantle is heated by the core’s extreme heat, the rock becomes lighter and rises. When the rock cools, it becomes heavier and sinks. This process is called convection. It’s why rock in the mantle is always moving. As the mantle moves, land on the surface also moves little by little. It’s like the land is dragged along by the mantle.
Is the Earth moving really fast?
The Earth circles the sun. This circling is called an orbit. It takes a full year to make a complete orbit of the sun. So how fast do you think the Earth is moving in its orbit? Can you believe it’s moving at a speed of 30 kilometers per second? That’s amazingly fast.
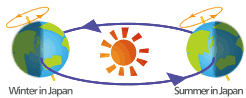
The Earth also spins around itself, as it orbits the sun. This is called the Earth’s rotation. The Earth completes a full rotation in one day. At any given time, the side of the Earth lit by the sun is in daytime. The other side where the sun’s light does not reach is in nighttime. The reason each day has daytime and nighttime is because of the Earth’s rotation.
The Earth rotates around itself at an angle of 23.4 degrees as it orbits the sun. Because of this, the direction of the sun as seen from Earth continually changes during the Earth’s orbit. This is what gives the Earth the four seasons.
Why does the Earth’s temperature change?
We know the Earth’s circles around the sun at an angle of 23.4 degrees. This is why the angle at which sunlight hits the Earth’s surface gradually changes over the course of a year. This is what causes the seasons to change. Let’s look at this process in a little more detail.
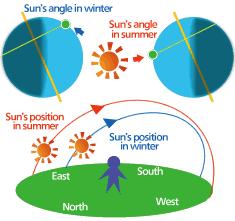
The sun’s height in the sky and where it rises and sets changes, depending on the season. On the day of an autumnal equinox or a spring equinox, the sun rises in the true east and sets in the true west. Daytime and nighttime are exactly the same length on these days. On the day of a summer solstice in the northern hemisphere, the sun is at its highest in the sky and daytime is the longest. This is why summers are hot. On the day of a winter solstice, the sun is at its lowest in the sky and daytime is the shortest. This is why winters are cold.
Besides the seasons, temperatures change depending on what latitude you are at. Near the equator, the sun shines directly overhead, making temperatures higher. At higher latitudes, the sun shines at an angle, so the temperature is lower. The Earth can be divided into tropical, temperate, and polar climate zones, depending on the latitude.
Why doesn’t the Earth run out of water?
Have you ever wondered why the amount of water on Earth doesn’t run out? Or have you ever wondered whether the oceans will overflow? Interestingly, the amount of water on Earth always stays constant, not decreasing or overflowing. This is because water changes state and cycles around through many different places.
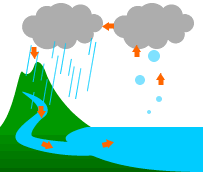
Water on the surface of the ocean is heated by the sun and turns into water vapor. The water vapor rises into the sky, where it cools and forms clouds. It then turns into rain or snow and falls back to the Earth’s surface. The water flows over the land, passes through rivers, and returns to the oceans again. This repeating cycle is called the water cycle. Water has been constantly traveling through the sky, land, and oceans for millions of years.
What will happen to the Earth at the very end?
The Earth has a lifespan like everything else. Its lifespan is closely related to the sun. The sun is always shining light on the Earth. But the sun will not shine forever.
The sun’s lifespan is said to be about 10 billion years. The sun has gotten brighter by about 1 percent every 100 million years. About 500 million years from now, because of the sun’s increasing heat, the Earth’s seawater will have evaporated and no life will be able to live on the Earth. And about 5 billion years from now, the sun will have expanded out so far that it will swallow the Earth.
At the very end, the sun will explode. Everything will go back to being gas and dust. It’ll be just like before the sun and the planets in our solar system were formed. But because of the sun’s explosion, the gas and dust will be scattered throughout the universe and become the materials for the birth of a new star.
Is it true people in ancient times didn’t know the Earth is round?
The Age of Discovery began in the 14th century, when Europeans began sailing the seas all over the world. As they discovered new sea routes and continents, they also figured out the Earth is a round, spherical planet.
Still, they believed the sun and stars revolved around the Earth. The astronomer Copernicus was the first to say that the Earth and other planets circle around the sun. Still at the time, no one believed the Earth revolved around the sun.



