Ways of Thinking about Water Resource Conservation
It is said that available fresh water is only about 0.01% of the Earth's total water resources. We understand that the water crisis is one of the global risks, considering further increase in water consumption because of economic growth and population increases in near future.
As risks of extreme water shortages is becoming higher as one of social issues, the Panasonic Group has been working to conserve water resources both in its products and production activities, in order to fulfill its social responsibility and to reduce risks in the management. Our Environmental Policy sets that we make efforts to conserve water resources by using water efficiently and preventing water pollution. We are working hard to reduce water usage in our business activities and through our products and services by setting water resource conservation in Our GREEN IMPACT PLAN 2024+1 as one of the continuing efforts.
For promoting these activities, the Panasonic Group have established a structure for the promotion of environmental management, including water management. We are continually working to develop our environmental sustainability management by implementing the PCDA management cycle. We have also created an environmental risk management organization to identify environmental risks each fiscal year and continue to reduce them. This organization promotes risk management across the Group and is working on ways to implement rapid action when an environmental risk emerges.
These efforts are also based on the position that access to sanitary water is a fundamental human right.
Moreover, the Panasonic Group has participated in the Water Project, a public-private partnership project aimed at boosting awareness of water conservation, which was launched under the initiative of Japan's Ministry of the Environment in 2014. Objectives of the project are to maintain a sound water cycle and promote its recovery. The project distributes water-related activities conducted by corporations, and water-related information including importance of water. The Panasonic Group will work in cooperation with the Japanese government and other companies to conserve water resources.
LEAP analysis of water resources based on the TNFD Framework
Although our Group had already implemented a water risk assessment by fiscal 2018, we have started to reassess the risks in view of evolving assessment standards and changes in the business environment. We are presently working on identifying and assessing risks related to water resources and their impact, in compliance with the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) Framework. As part of this effort, we are conducting systematic risk assessment based on the LEAP Approach*1 at all of our manufacturing sites.
The first phase of the process is "Locate," which defines the relationship between our site's location and natural capital. Specifically, we use the water risk assessment tool Aqueduct from Water Resources Institute (WRI) and Water Risk Filter from the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) to assess the position of each of our manufacturing site vis-à-vis the natural environment and have conducted assessments of water stress and water quality contamination risks. As a result, we have been able to identify sites where water resources face high levels of physical risk. On some of these high-risk sites, aggressive action is already underway to reduce the physical risks. These cases are presented on our website.
In the subsequent "Evaluate" phase, a detailed review is conducted of sites that are identified as having a high dependence on water collection (type, usage, water withdrawal, etc.) and the impact caused by effluent discharge (discharge method, discharge destination, proximity to protected areas, etc.). This study enables us to evaluate each site's dependence on water resources and its impact on the natural environment. The "Assess" phase is designed to identify clearly the projected risks and opportunities based on the assessment results. At the "Prepare" phase, we decide how to apply our findings to defining effective targets and developing countermeasures.
*1 LEAP approach
TNFD adopted the LEAP approach to comprehensively assess nature-related risks and opportunities.
The LEAP approach comprises four phases: Locate the company's interfaces with nature; Evaluate its dependencies and impacts on nature; Assess its nature-related risks and opportunities; and Prepare and report on material nature-related issues.
Water Stress Risks (Percentage of High-Risk Site)
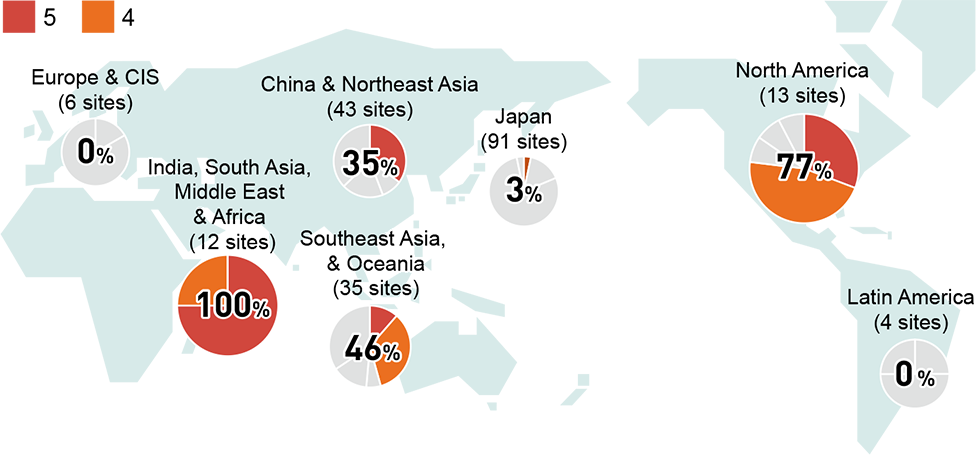
*Excluding the factories within Panasonic Automotive Systems Corporation, which was deconsolidated in December 2024
Water Pollution Risk (Percentage of High-Risk Site)
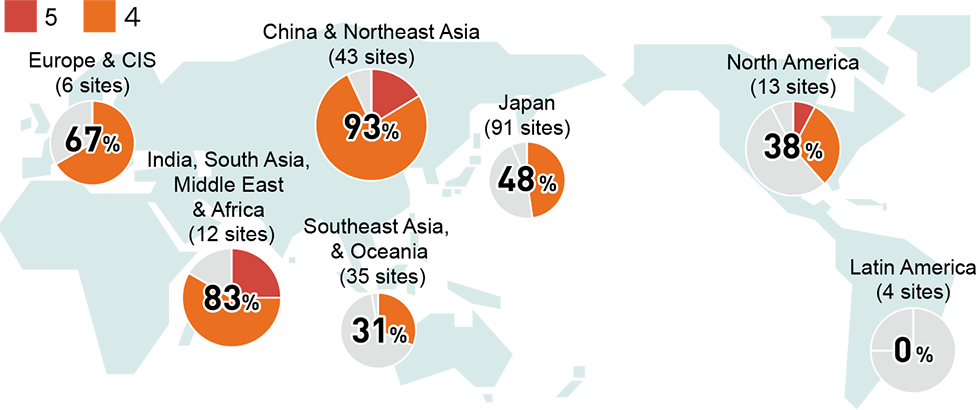
*Excluding the factories within Panasonic Automotive Systems Corporation, which was deconsolidated in December 2024
Efforts to reduce risks at sites with high physical risk regarding water resources
PT. Panasonic Gobel Energy Indonesia
PT. Panasonic Gobel Energy Indonesia has started an initiative to reuse condensate from RO (reverse osmosis membrane) systems, which was previously discharged, as water for cooling towers. This reuse not only reduces the amount of water required to operate the cooling towers, but also reduces electricity consumption and the amount of chemicals used for water treatment.
Through these efforts, they have reduced their water consumption by approximately 23,904 m3 per year, and CO2 emissions by 10.44 tons per year.
Panasonic Life Solutions India Pvt. Ltd. Kutch Factory
The Kutch Factory of Panasonic Life Solutions India Pvt. Ltd. is located in an arid desert area, where water is procured by tanker trucks.
The Kutch Factory is located in an area of India where water is quite valuable and expensive, so they are actively promoting the reuse of rainwater and automation of the water supply system. First, the roof of the raw water tank was renovated and improved so that it could efficiently collect rainwater. The collected rainwater is reused for gardening, the driver's waiting room, and hand washing in the cafeteria area. In addition, there was previously no control function for sending water from the raw water tank to the tank at the factory, which caused issues with water overflowing when supplying water.
To address this issue, automatic operation functionality was introduced to enable them to properly control the water level of the tank and prevent water from overflowing. In addition, a new submersible pump was introduced for transporting the water, achieving conservation of both water and energy. Through these efforts, they were able to reduce water consumption by approximately 154 m3 per year, resulting in cost savings of 15,076 INR.

Panasonic Home Appliances Refrigerator (Wuxi) Co., Ltd.
Panasonic Home Appliances Refrigerator (Wuxi) Co., Ltd. is strengthening its wastewater and rainwater management systems and actively promoting environmental conservation initiatives.
To start, they are carrying out a complete renewal of drainage pipes and related facilities, and are strictly controlling the separation of drainage pipes and storm drains through regular testing and maintenance.
They are also periodically checking the quality of rainwater to ensure that it remains in an appropriate condition. Identification labels are also affixed to all rainwater wells in the workplace to prevent the dumping of waste by people.
In addition, new shutoff devices and collapsible emergency pools have been installed at the storm drains, and regular drills are being conducted to prevent runoff in the event of contamination.

Panasonic Corporation Living Appliances and Solutions Company Hikone Factory
The Hikone Factory of Panasonic Corporation Living Appliances and Solutions Company is implementing a variety of measures to minimize its impact on the water environment.
First, they have established their own standards for measuring water quality that are stricter than the standards set by prefectural and municipal ordinances, and are managing water quality at a higher level.
They also provide annual training on environmental laws and regulations for departments that have specified facilities related to the Water Pollution Prevention Act and for environmental promotion personnel in each department to improve compliance with laws and regulations as well as increase environmental awareness.
As part of their wastewater management system, they have installed wastewater monitoring panels equipped with a pH meter, turbidity meter, and UV meter to monitor wastewater 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
When an abnormal value is detected, an alarm is issued from the monitoring equipment and a system is in place to respond promptly.

Panasonic Corporation Living Appliances and Solutions Company Panasonic Resource Recycling Factory Kato
At Panasonic Corporation Living Appliances and Solutions Company's Panasonic Resource Recycling Factory Kato, instead of the conventional wet cleaning method, a dry cleaning method has been adopted in the cleaning process of recycled resin that does not use any water at all. Wet cleaning carries the risk of microplastics contamination in wastewater, and dry cleaning can significantly reduce this risk.
This dry cleaning system is a repurposed rice milling system and has been installed on a limited basis at the Kato Factory and some outside partner companies. This highly unique approach reduces water use and prevents the release of microplastics. These measures are effective approaches to two important environmental issues: the conservation of water resources and the prevention of marine pollution.
Water Resource Conservation through Products
By thoroughly analyzing the use of water through our products, we have developed functionalities that allow a considerable amount of water conservation by utilizing water at a maximum level through improvement of water flow control and cyclic use. We continue to develop products with low water usage.
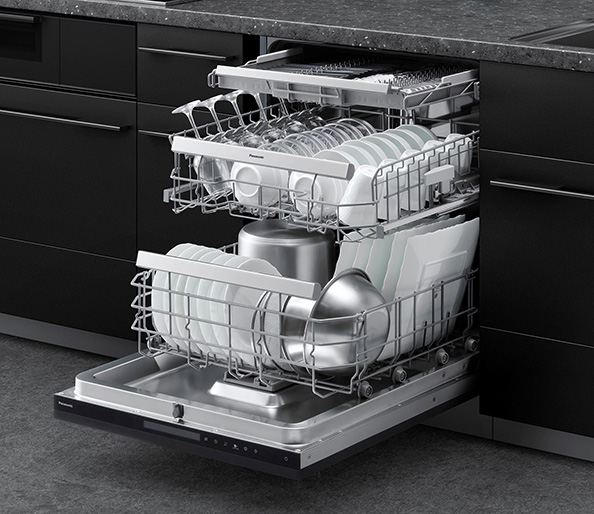
Dishwasher/Dryer (Front Open Type)
The front-open dishwasher NP-60EF1W has a large capacity that can hold dishes for 12 people, and can wash dishes for a day at a time. This reduces the burden of housework for users and contributes to reducing water consumption during dishwashing. The amount of water used is approximately 1/9 compared to washing hands (approximately 133.6 L for washing hands, approximately 15.1 L for saving about 59 2 L plastic bottles), contributing to water conservation during washing dishes. When electricity, gas, water, and detergent used for washing dishes and washing hands are converted into CO2 emissions (calculated by our company), the amount of CO2 emitted by the dishwasher is smaller.
In addition, the product washes dirt thoroughly with the high cleaning power of high-temperature, high-pressure water flow, eliminating the need for pre-washing before setting dishes. The newly constructed Residue Filter uses our company's proprietary technology to use an automatic cleaning system that cleans the filter at each step during washing. This reduces the frequency of maintenance after operation.

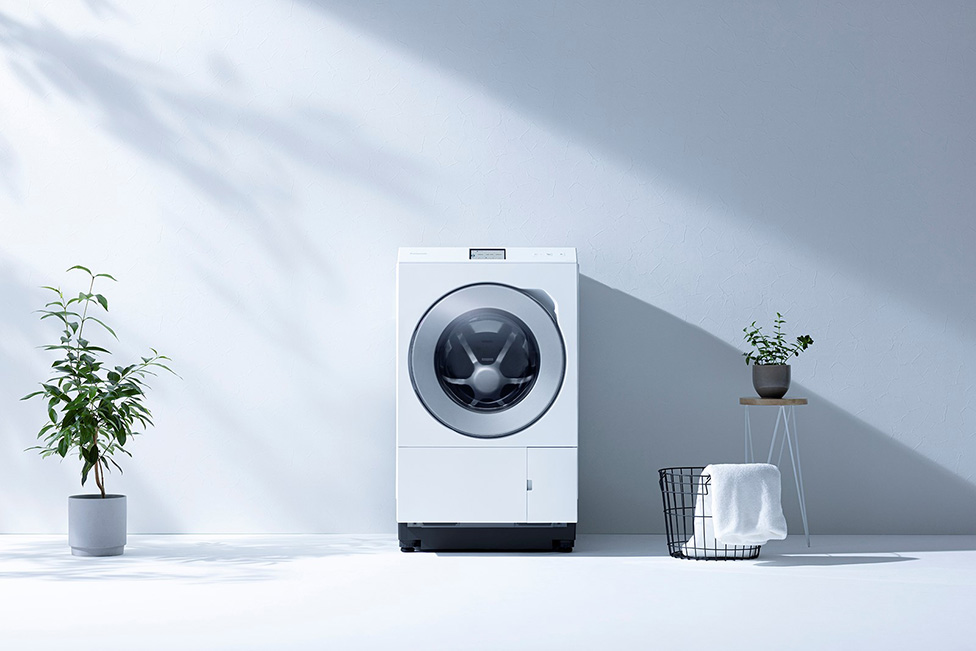
Flat Drum Washing and Drying Machine LX Series
Compared with vertical washing machines, the LX series of slick drum washers and dryers can save about 30% of electricity consumption during washing and about 67 L of water used, thereby contributing to the conservation of water resources. Considering the energy required for water treatment in tap water and sewage, saving water also contributes to reducing CO2 emissions. In addition, the triple automatic injection of liquid detergent and softener prevents excessive use of detergent, thereby reducing environmental impact. By using the extra-large refill type, the amount of plastic used in detergent containers can be reduced by about 88%.

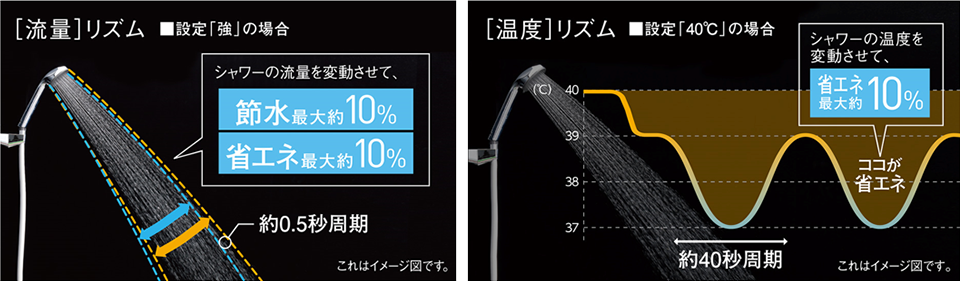
Rhythm e Shower Plus
By changing the flow rate and temperature of the shower at a constant rhythm, we achieved energy savings of up to 20% and water savings of up to 10%.
A single sensor and flow sensor detect the use of the shower and a flow control valve and control technology allow the shower flow to fluctuate at high speed.
*Rated on our company's own terms. The numbers are strictly nominal and vary depending on usage.
*According to JIS C 9220 load condition of household heat pump water heater at our company test facility. Summer hot water heating mode Heating conditions: Outside air temperature (dry-bulb temperature/wet-bulb temperature) 25 degrees C/21 degrees C Water temperature 24 degrees C Hot water set temperature 40 degrees C Direct hot water supply and shower use time 5 minutes/time (when using bathroom shower only). Total shower flow: Rhythm e Shower Plus ON (setting: strong) 45 L/OFF 50 L JP, J, W, FP, F Series Energy saving in full auto: Rhythm e Shower Plus ON (setting: strong) 2.6 MJ/OFF shower heat 3.3 MJ Water saving condition: Rhythm e Shower Plus ON (setting: strong) 8~10 L/min Shower flow in OFF 10 L/min

Flat range hood with cleaning function
The range hood is easy to get greasy stains and uses about 28 liters of water per cleaning.
Equipped with ECONAVI, the DW series flat range hood with washing function automatically cleans greasy dirt collected by the fan filter by simply filling hot water in the hot water tray, setting it in the main body and pressing the "wash" button. Cleaning every 2 months or so allows cleaning without removing the fan filter for 10 years. About 99% less water than conventional care *2
The DE series, which went on sale in September 2020, not only prevents oil from sticking to the blades because of its unique coating that repels oil from sticking to the blades, but also reduces blade cleaning to about once every 3 years *3 thanks to the "oil tornado function" that spins the fan at high speed to release oil stains on the blades by centrifugal force before the end of operation.
*2 The amount of water used is based on the company's own standards. Comparison of water volume between monthly (twice every two months) conventional care and bimonthly automatic cleaning
*3 Comparison of oil collection efficiency (range hood fan) test of filters of Better Living Quality Housing Parts Evaluation Criteria Ventilation Unit (kitchen fan)

Fully Automatic Cleaning Toilet "Arauno"
The Arauno, a fully automatic cleaning toilet that washes with foam every time it is flushed, uses water efficiently using a unique water-saving technology called the Turn Trap System, which reduces the amount of water used annually by approximately 40% *4 compared to conventional toilets. In addition to using a new organic glass-based material that does not easily stick to stains, the Triple Stain Guard, which reduces stains, reduces the number of cleaning times, thus saving water when cleaning.
The Arauno has a streamlined design and is also being used in stores and hotels where toilet space coordination is considered, expanding opportunities for water-saving beyond residential use.
*4 Comparison with toilets around 2000


Initiatives for Water Resource Conservation through Production Activities
By collecting and reusing wastewater from our manufacturing processes and air conditioning systems, the Panasonic Group has been reducing the amount of makeup water used and wastewater effluent. Through these activities, we reduce environmental loads on water resources due to the intake and effluent of water in production activities. As many regions around the world are threatened by water shortages, the Panasonic Group has been conducting production activities, balancing water resource conservation in focused regions. The amount of water withdrawal*5 at factories in fiscal 2025 resulted in 13.49 million m3, which is reduced by 2.7% versus the fiscal 2024. The water withdrawal at our factories per basic unit of production*6 deteriorated year-on-year due to the structural reform. Our use of recycled water*7 in fiscal 2025 was 1.4 million m3, accounting for 10.4% of the total amount of water withdrawal. The amount of discharged water in fiscal 2023, 2024 and 2025 resulted in 11.78 million m3, 10.60 million m3, 10.45 million m3 respectively.
*5 Change from "Water consumption" to "Water withdrawal" in reference to GRI standards
*6 Water withdrawal at factories per basic unit of production = Water withdrawal at factories/Production volume.
*7 The calculation excludes the water circulating for a single purpose (e.g., water in a cooling tower).
Water Withdrawal in Production Activities and Water Withdrawal Per Basic Unit
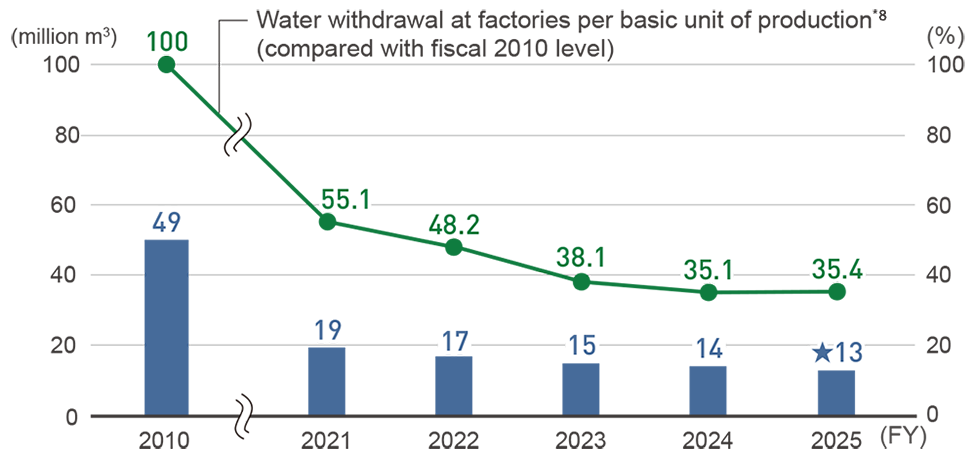
*8 Then-SANYO Electric and Panasonic Liquid Crystal Display not included in fiscal 2010
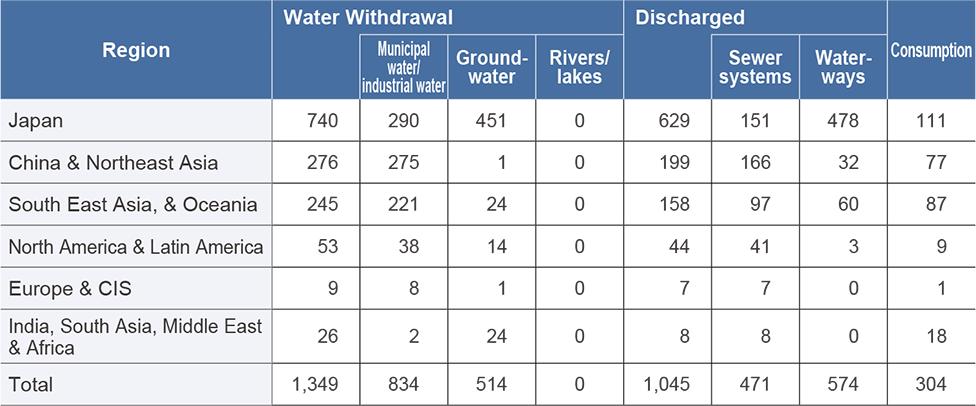
FY2025 Breakdown of Water Use (by region)
(10 thousand m3)
Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd. (52 sites), uses the highest amount of water in all operating companies in the Panasonic Group. The company managed to achieve a year-on-year decrease of 1.7 % in water withdrawal (5.32 million m3) in fiscal 2025, thanks to their focused efforts to reduce water withdrawal. The achievement rate for reducing the amount of water withdrawal per basic unit by using recycled water in factories, etc., was 103%.
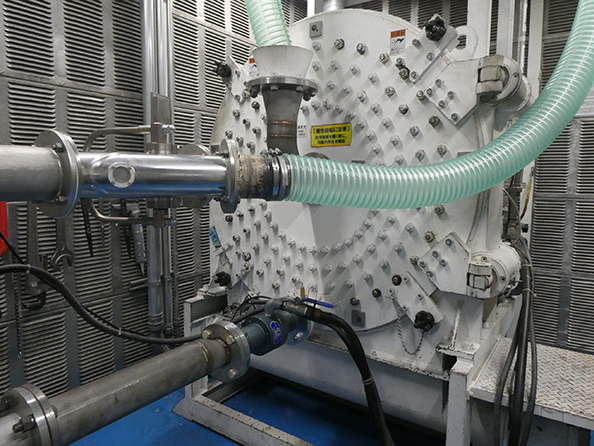
Against the backdrop of the increasing occurrence of natural disasters in recent years, such as earthquake and flood disasters, Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd. Saga site achieved a reduction of environmental risk and environmental impact, considering a possible chemical leakage from the outdoor storage site in the company premises. This was accomplished by replacing their water purification system, which used a chemicalbased regeneration method for the ionexchange resins, to a system that uses an electrical regeneration method.
At the same time, the company installed a wastewater collection system that separates the wastewater generated by the water purification into concentrated wastewater and collection water. The company is now able to reduce the water consumption for the entire factory by 61.8 thousand m3 per year by reusing the collection water.
The Panasonic Group will continue our efforts to conserve water resources.

Device Solutions Business Division Saga, Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd.

Water purification system with electrical resin regenerator


