Intellectual Property
-
Policy
-
Responsible Executive and Framework
-
Intellectual Property Strategy Framework
-
Mechanisms for Consolidating Patents and Other Assets to Create Group Synergies
-
Acquiring Intellectual Property Rights and Reward System
-
Respect for Intellectual Property of Third Parties
-
Contributions to Building Co-creation Relationships
-
Co-Creation Contribution to Solving Societal Challenges
-
Participation in International Initiatives
-
Anti-Counterfeit Activities
-
In-House Education and External Consumer Awareness-Raising
-
Consultation & Whistleblowing
-
Evaluations
Panasonic group strives to appropriately acquire, protect, and utilize technologies, know-how, designs, brands, and other achievements obtained through R&D and other business activities as intellectual property.
By implementing our group’s intellectual property in various ways, such as commercialization in our group and co-creation with other companies as well as striving to respect the intellectual property of third parties in our group’s business activities, Panasonic Group aims to achieve business growth in our group and achieve solutions to social issues.
Policy
Based on the spirit of “IP (intellectual property) before business” since its founding, Panasonic Group has been promoting intellectual property activities, aimed at ensuring the advantage and safety of its business now and in the future and helping address social issues, by proposing IP-based strategies for its business; acquiring, protecting, and utilizing global intellectual property; and preventing and resolving disputes related to intellectual property.
To consistently achieve these goals, the Group has established its “Basic Rules for Intellectual Property Matters” that apply to the entire Group. We are working to appropriately pursue our intellectual property activities and establish a foundation for our initiatives. In addition, we respect the intellectual property of our suppliers, business partners, and other third parties and do our best not to infringe on them. That is also a stipulation in the “Panasonic Group Compliance Code of Conduct,” and we provide regular education to ensure that all employees comply with it.
Responsible Executive and Framework
The Group Chief Technology Officer is the executive officer responsible for intellectual property for the Group (as of August 2025).
The Intellectual Property Department at the Group’s holding company, Panasonic Holdings Corporation (PHD), is in charge of establishing and promoting the Group’s intellectual property strategies. We have also established an intellectual property division at each Operating Company, and each intellectual property division establishes and promotes intellectual property strategy of each Operating Company. PHD's Intellectual Property Department and the intellectual property divisions of each operating company work together to promote intellectual property strategies, thereby creating group synergy.
In addition, the Intellectual Property Department at Panasonic Operational Excellence Corporation ("PEX") which has highly specialized personnel, and Panasonic IP Management Corporation ("PIPM"), a subsidiary of PEX, are advancing a wide range of intellectual property operations on a global basis.
PIPM was established as a wholly owned subsidiary to integrate and commercialize the Group's intellectual property operations, and is advancing intellectual property operations by utilizing the "Trusts among Persons Belonging to Same Group of Companies" as stipulated in Article 51 of the Trust Business Act.
Intellectual Property Strategy Framework
The Group has formulated an Intellectual Property Strategy Framework through discussions at Board of Directors meetings (see the figure below). This framework shows that our intellectual property (IP) strategies and activities, conducted from the perspectives of "customers," "competitors," and "society" based on our materiality, will contribute to "business advantages" and "business safety" as well as "social implementation through Co-creation with intellectual property as a starting point", and that these will contribute to solving social issues and ultimately lead to the vision we are aiming for.
These strategies and activities are embodied in the framework based on each aspect of intellectual property: "rights," "assets," and "information."
For example, from a "customer" perspective, strategies and activities such as planning and implementation of "co-creation and open & closed strategies" and "IP portfolio (PF) building of core technologies", will lead to output in the form of "improvements in customer value."
From the "competitors" perspective, strategies and activities such as "dispute resolution", "strict respect for third-party IP", and "lean transformation of our IP portfolio (e.g., abandoning unnecessary IP)" will lead to output in the form of "improvements in cost performance."
From the "social" perspective, strategies and activities such as "Co-creation with intellectual property as a starting point" will lead to outputs such as "social implementation through co-creation" (e.g., commercialization of environmental technologies through co-creation with other companies).
These outputs will lead to our goal of realizing "an ideal society with affluence both in matter and mind."
PHD has introduced "Group-common Indicators of Intellectual Property" shared across the Group to monitor each IP strategy and activity indicated in the framework. These "Group-common Indicators of Intellectual Property" include, for example, utilization indicator that illustrates the size of IP assets (i.e., intangible assets) and how they are being used (their degree of circulation). We use these "Group-common Indicators of Intellectual Property" to monitor the IP strategies and activities of each operating company and maximize the value of our intangible assets.

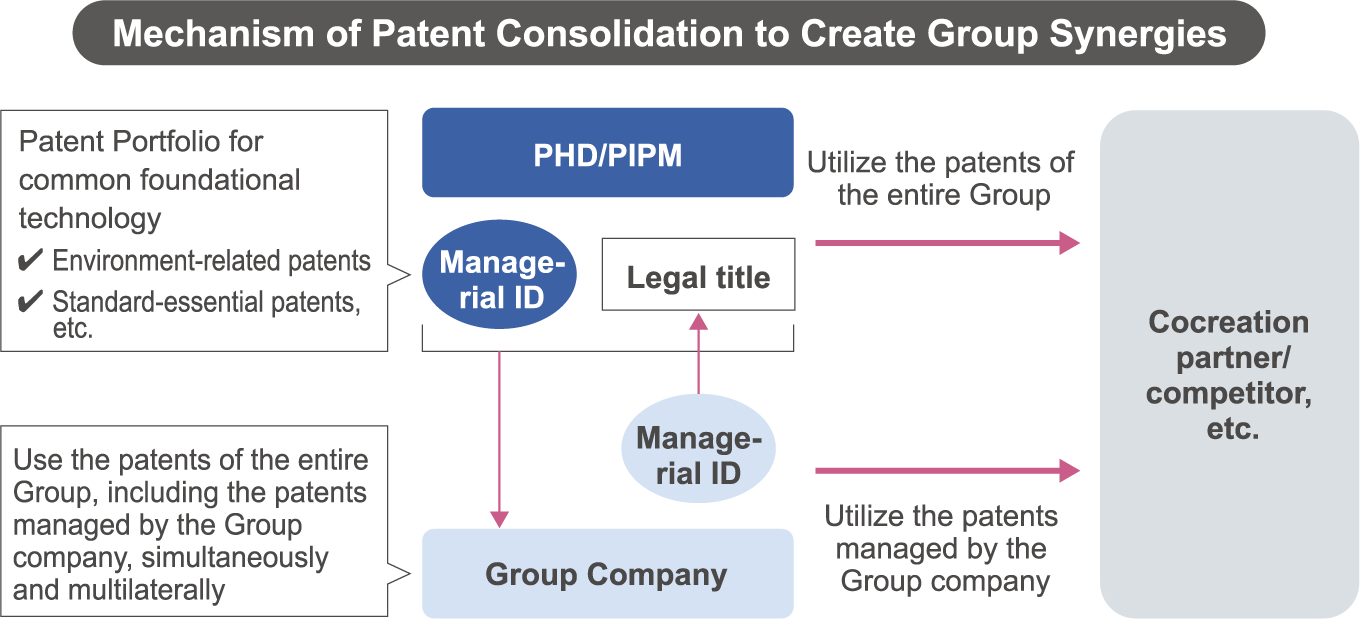
Mechanisms for Consolidating Patents and Other Assets to Create Group Synergies
The Group has set up a mechanism to consolidate patents and other forms of industrial property to PHD so that they can be utilized as assets of the entire Group simultaneously and multilaterally. PHD and its subsidiary, PIPM utilize (e.g. license) the patents, etc. of the entire Group. These include patents related to common foundational technology and patents with legal title consolidated from our Group companies. The Group companies in Japan that are subject to this mechanism manage the patents, etc. they have created or obtained (i.e., they retain the “Managerial ID” (Managerial code) as the identification of responsibility for managing such patents, etc.), and such Group companies bear the costs and receive the revenues from them, even after their legal title has been consolidated to PHD. The Group company can then use the patents, etc. of the entire Group, and externally utilize those for which it holds the Managerial ID. The Group promotes both internal and external co-creation, etc., using this mechanism (see figure below).
Acquiring Intellectual Property Rights and Reward System
Panasonic Group has been building up a global portfolio of intellectual property in line with our IP strategy, which in turn is based on our business strategies and research and development strategies. The following table shows the fiscal 2025’s R&D expenses; the number of new applications for patents, utility models, or design rights made by Panasonic Group in fiscal 2025; and the number of patents, utility models, designs, and trademarks held by the Group as of March 2025.
| R&D expenses in fiscal 2025 | 477,800 million JPY (the ratio of R&D expenses to sales: 5.6%) |
|---|---|
| Number of applications in fiscal 2025 | Number of applications for patents, utility models, and designs: Total roughly 16,000 (including roughly 9,000 outside Japan) |
| Number of rights held as of March 2025 | Number of patents, utility models, and designs held: Total roughly: 95,000 (including roughly 53,000 outside Japan) |
| Number of trademarks held: Total roughly 15,000 (including roughly 11,000 outside Japan) |
If the Group's intellectual property is not properly protected and utilized, counterfeit or infringing products involving that intellectual property may emerge, causing quality problems, generating inflows of funds to criminal organizations, and other problems that may inhibit sustainable innovation. Going forward, the Group will continue to acquire the results of research and development and business activities in the form of intellectual property, and will strive to further protect and utilize intellectual property.
The Panasonic Group also has a reward system for inventors designed to increase their motivation and help invigorate their inventions and creative endeavors, and we operate this system in a just and fair manner based on the laws and regulations of each country. For example, in Japan, the standard for reward is decided through agreements with employees and shared with them, and we also have a system in place to solicit feedback from inventors about the reward system.
Respect for Intellectual Property of Third Parties
If we infringe on the intellectual property of a third party, there is a risk of causing losses to that third party and inconvenience to our direct and indirect customers due to changes in specifications or interruptions in the supply of our products or services.
The Group conducts its business activities while striving to respect third parties' intellectual property. Our Groupwide internal rules stipulate how to respond when a third party contacts us with a suspicion of intellectual property rights infringement and how to estimate losses in the event of such infringement. The internal rules of each Operating company also stipulate how to conduct investigations, report discovered risks, and follow other processes to prevent infringement of third-party intellectual property rights.
Contributions to Building Co-creation Relationships
The Group aims to contribute to solving social issues in its business activities. In addition to facing social issues head-on, contributing to their resolution, and growing our business as a result, we are also promoting a new intellectual property strategy by building a system that connects and cooperates between a wide range of people, goods, and things, and building co-creation relationships based on intangible assets to solve social issues that are difficult for individual companies to address.
Specifically, in September 2023, we opened "Technology Index" for external use. The Technology Index is a system that enables users to easily find and connect with the technology they need by indexing the Group's intellectual property information in easy-to-understand, sensible language that describes the technology's usage scenarios and purposes. Taking the Technology Index as a starting point, we will contribute to accelerating the resolution of social issues, including the resolution of global environmental problems, by circulating intangible assets throughout society.
Additionally, in October 2024, we launched IP Junction, a co-creation and innovation hub for intangible assets. IP Junction is a platform for distributing and matching information that assists in co-creation with all our partners who have diverse technologies and ideas so that we can expand the use of shared knowledge accumulated through the Technology Index. We collect, index, and link data on intangible assets within and outside the Group to facilitate the sharing of intangible assets and accelerate the creation of shared knowledge.
Co-Creation Contribution to Solving Societal Challenges
As mentioned above, our group announced its long-term environmental vision, “Panasonic GREEN IMPACT (PGI)”, in January 2022. Since then, we have been accelerating efforts to reduce the environmental burden across the entire value chain while also contributing to the reduction of CO2 emissions for society and our customers. The “CONTRIBUTION IMPACT” of PGI refers to our contribution to reducing CO2 emissions in society and for our customers through the provision of our own products and services. At the same time, our group holds a large portfolio of intellectual property related to environmental technologies, and we aim to promote social implementation and contribute to solving societal challenges by strategically building co-creation partnerships with other companies.
For example, by allowing our intellectual property to be used by our co-creation partners in the field of vehicle batteries, we are helping to reduce CO2 emissions by replacing gasoline-powered vehicles with electric and hybrid vehicles.*1 Similarly, by allowing our co-creation partners to utilize our intellectual property in high-performance vacuum insulated glass, the technology has been adopted for building window materials, replacing single-pane and double-pane glass, thereby contributing to CO2 reduction.*2 For example, we estimate that in 2023, the effects of CO2 reductions of electric vehicles equipped with lithium-ion batteries using our intellectual property is 9.78 million tons of CO2 emissions.*3
Our group is also actively engaged in the development of future environmental technologies and holds a substantial portfolio of intellectual property.
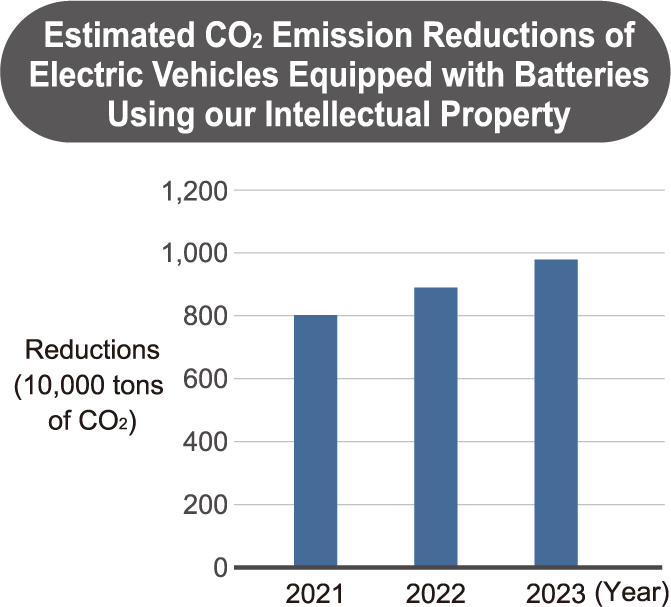
Through these efforts, we aim to continue contributing to the dissemination of sustainable technologies and the reduction of CO2 emissions. For example, we commissioned astamuse company, Ltd. to conduct a carbon reduction potential analysis*4 of environmental technologies, and our group’s technologies were featured in their published report.*5
Addressing societal challenges such as climate change is not something our group can tackle alone. Panasonic Intellectual Property Division will continue to promote social implementation and aim to contribute to solving societal challenges by building co-creation partnerships with other companies, leveraging intellectual property as a starting point.
*1 CO2 reductions from automotive batteries: The difference in CO2 emissions during running (using) between gasoline-powered vehicles and electric vehicles equipped with batteries that incorporate our intellectual property.
*2 CO2 reductions from vacuum insulated glass: The difference in CO2 emissions from the energy required to operate air conditioning systems when using vacuum insulated glass incorporating our intellectual property, compared to single-pane or double-pane glass.
*3 The flow method (emissions for the entire lifetime of the vehicle are accounted for in the year of sale) is used to calculate the difference in CO2 emissions during running (using) between a gasoline-powered vehicle and an electric vehicle equipped with batteries using our intellectual property. The CO2 emissions from battery production were calculated and subtracted from the total. Compared to last year’s estimate, we refined the baseline data—such as fuel efficiency for gasoline vehicles and energy efficiency for electric vehicles—for greater accuracy. All graphs were calculated based on the same methodology across all years.
*4 Based on investment data and other sources, astamuse company, Ltd. analyzes carbon reduction challenges primarily from a technological perspective. The company provides a comprehensive overview of technologies that contribute to solving these challenges and quantitatively evaluates the “carbon reduction potential” of each technology.
*5 https://www.astamuse.co.jp/news/2025/250509_cn/ (Japanese only)
Participation in International Initiatives
WIPO GREEN, established by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) supports global-scale approaches against climate change through connecting key stakeholders when it comes to environmentally-conscious innovations using its database and networks. The Panasonic Group agrees with this mission and has registered environmentally-conscious underwater plasma technologies, artificial photosynthesis technologies, and gas sensor technologies.
Anti-Counterfeit Activities
Counterfeit products that use important corporate assets such as brands and other intellectual property without permission, and piggyback on the brand value built up by the rights holders not only cause quality problems (accidents and injuries) for customers, but also give rise to the following problems for society as a whole and can be an obstacle to the creation of a healthy society.
- Economic losses: decreasing tax revenues, less business incentives to develop new products and innovation.
- Security issues: potential sources of funds for criminal/ terrorist organizations, increasing threats to national security.
- Environmental problems: disposal of seized counterfeit goods
Thus, aiming to eliminate counterfeit goods should be considered a Corporate Social Responsibility. Our anti-counterfeit policies aim to solve the social issues caused by counterfeit products and protect our customers and intellectual property, including brands. In 2019, measures against counterfeit products were added to the Japanese government’s SDGs Action Plan, thanks in part to advocacy from the Panasonic Group. At present, we are working in partnership with the Japanese government, other companies, and the governments of other countries at the International Intellectual Property Protection Forum (IIPPF), an industry organization that aims to resolve the counterfeit issue, to take action based on the idea that eliminating counterfeit products will contribute to achieving SDGs. Recent trends show a rapid increase in the number of counterfeit goods sold online, in addition to those sold in actual markets. Online sales make selling counterfeit products easier globally than conventional retail methods— transactions are made easily and carried out before the buyer ever sees the actual product, meaning that there is an increasing risk that consumers could purchase them by mistake. Panasonic Group believes that it is more critical than ever that rights holders work together with consumers to eliminate counterfeit goods and work aiming to create a better world. In recent years, we have begun posting monthly updates regularly on social media to engage with the growing number of users on these platforms.
Example) https://twitter.com/PanasonicBrand/status/1759463303867466126 (Japanese only)
In-House Education and External Consumer Awareness-Raising
Panasonic Group conducts various training and education programs for employees to ensure they thoroughly implement Panasonic’s policy on intellectual property. Alongside the above-mentioned employee education on respecting third-party intellectual property, we provide e-Learning on copyright for employees in Japan and overseas, taking into account importance of software in business and the rapid spread of generative AI in recent years.
In addition, each Operating Company also provides training and education on intellectual property to meet their specific business needs. For employees engaged in intellectual property operations, we provide a wide range of training and education with a view to achieving business success, including training on project management and training to improve IP-related expertise.
We also help raise awareness of intellectual property issues outside the Company. One such example is dispatching lecturers to HR development trainings for overseas governmental authorities such as patent office staff upon request by the Japan Patent Office. We also give our unique lectures on intellectual property at Japanese junior high and high schools. In addition, to address the issue caused by counterfeited products, we manufacture the consumer awareness videos and introduce them at our website.
Consultation & Whistleblowing
All Group employees, business partners, and their employees can seek consultation and report any intellectual property-related risks or problems they see or hear about through the global hotline Panasonic has set up. For more details, see the “Whistleblowing System” in the “Compliance” chapter.
Evaluations
Panasonic Group has been recognized as a Clarivate Top 100 Global Innovator 2025 chosen by London-based Clarivate. The award that Panasonic Group received is given to companies that are leaders in global business because they are successful in protecting and commercializing their unique inventions and ideas through intellectual property rights. Panasonic Group has been on this list since its inception, 2025 being our 14th consecutive year.
The Panasonic brands were also honored in Clarivate’s Top 100 Best Protected Global Brands (in 2021), a testament to the fact that the Group properly protects its brand. Furthermore, the Panasonic GREEN IMPACT brands were also honored in Clarivate’s Top 100 New Brands in 2023 as new brands that have surged into the public sphere since 2021 and demonstrated an exceptional ability to bring value, impact, and protection on a global scale.



