Reducing CO2 Emissions in Factories
Reducing the Amount of Energy Used and CO2 Emissions in Business Activities
To achieve Panasonic GREEN IMPACT, Panasonic Group has been working on toward making net zero factories*1 by promoting our efforts internally and externally to realize net zero CO2 emissions at own sites in all our operating companies by 2030.*2
For this medium term, we established the GREEN IMPACT PLAN 2024. As our efforts for OWN IMPACT Scope 1 and 2, we have increased the number of net zero factories to 37, aiming to reduce 260,000 tons of CO2 emissions. In the Net Zero Factory Promotion Taskforce we started up in September 2021. The taskforce aims to create and provide Group-wide measures to accelerate the creation of net zero factories. The Taskforce consists of the Energy Saving Working Group (WG) that promotes a range of energy-saving measures, the Renewable Energy Utilization WG that assess the usage expansion of renewable energy in each site, and the Renewable Energy Procurement WG that promotes the procurement of renewable energy. With the participation of related sectors, our manufacturing, procurement, and environment specialists work together to support the united efforts of all operating companies. During this fiscal year, we held seminars to introduce internal excellent examples and the latest information on energy saving and energy recycling to Group members. We also hold study session by region outside Japan.
We also participate in the Keidanren Carbon Neutrality Action Plan, a voluntary action plan to alleviate global warming promoted by the entire electric and electronics industry. The industry set a target of an "average 1% improvement in energy intensity in factories and large offices per year towards 2030" and we are now working steadily to save more energy in factories and offices.
*1 The Panasonic Group's net zero factories mean realization of net zero CO2 emissions from factory production across the world. This will be attained by promoting our conventional energy saving activities (e.g. using LED lighting), advanced energy saving technologies, such as Factory Energy Management System (FEMS), productivity improvement, and innovative manufacturing. Other means include a combination of the following efforts: promoting renewable energy usage, such as by adopting photovoltaic power systems, energy storage modules, and hydrogen fuel cells; procuring 100% renewable energy-sourced electricity; and obtaining environmental values (energy certificates and carbon credits). The Panasonic Group publishes, both internally and externally, our accelerating efforts towards reaching our goal of net zero CO2 emissions in all the operating companies' sites by 2030.
*2 Panasonic's direction: To become a top runner in the fields of "environment" and "high usability in business."
Increasing the number of net zero factories
After realizing the group's first net zero factory in fiscal 2019, Panasonic Group has realized 9 net zero factories in 5 regions*3 by fiscal 2022. Since then, it has entered the phase to increase the number of net zero factories: to 31 factories in fiscal 2023; 44 factories in fiscal 2024, in fiscal 2025 total 45 factories*4 - 19 factories in Japan, 14 factories in the China and Northeast Asia region, 5 factories in the Southeast Asia, Pacific, India, South Asia, Middle East, and Africa regions, 6 factories in the North America and Latin America regions, and 1 factory in Europe and CIS. This has exceeded the GIP2024 target of 'a total of 37 factories achieving net zero CO2 emissions'. (Excluding the 12 factories achieved in fiscal 2024 at Panasonic Automotive Systems Corporation, which was deconsolidated in December 2024)
Nishikinohama Factory, Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd. has achieved net zero CO2 emissions*5 since fiscal 2024 when it started operation of photovoltaic panels installed over the entire rooftop for maximum use of renewable energy, aiming at manufacturing in harmony with the environment. For introducing a 2 MW-class photovoltaic power generation system, a new method that does not require significant remodeling works of the transformer substation in the factory was invented and introduced, which contributed to achievement of significant reduction in the construction costs and the construction period.*6 The factory will further accelerate efficient and clean manufacturing by implementing energy management for the entire factory through installation of pure hydrogen fuel cell generators and energy storage systems for.

For more information on Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd.'s environmental initiatives at its factories, click here.
Global map of net zero factories
Global map of zero-CO2 factories
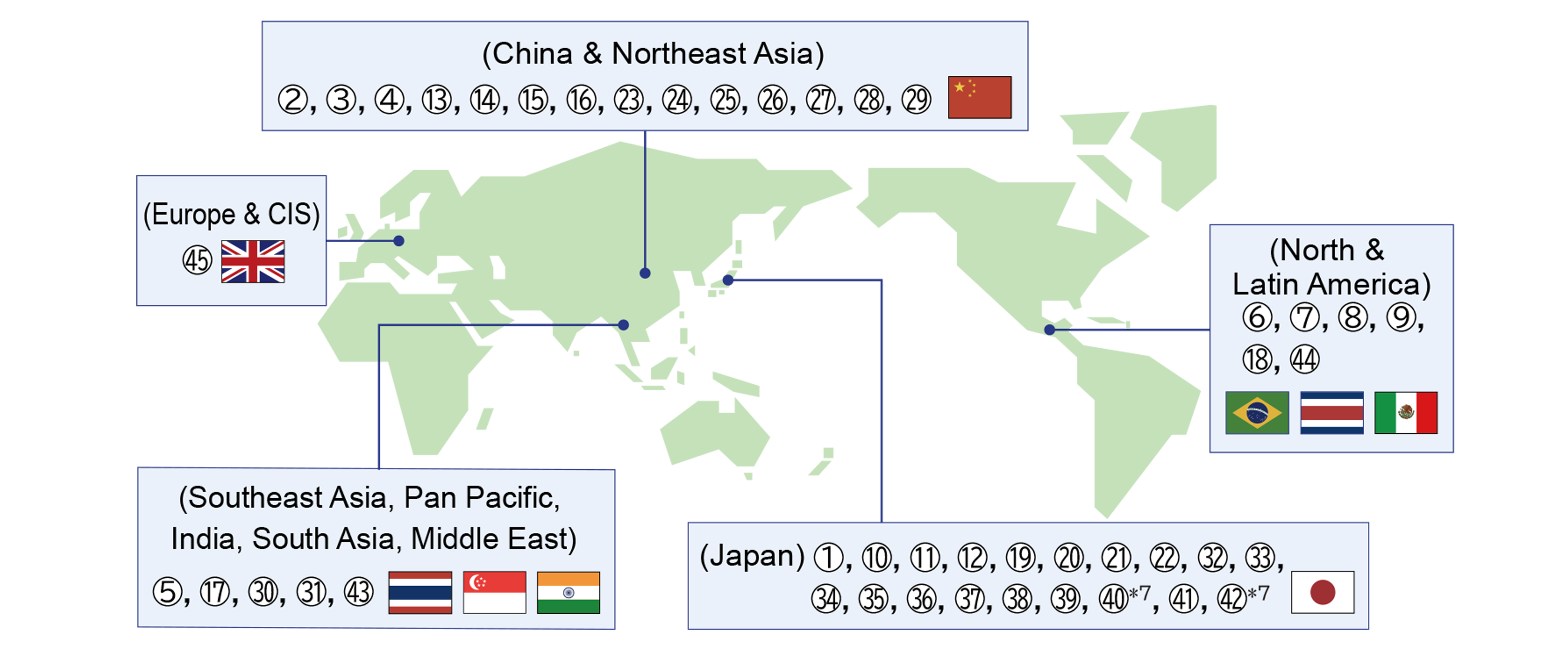
*3 Five regions are: Japan; China & Northeast Asia; Southeast Asia, Pan Pacific, India, South Asia, Middle East; North & Latin America; Europe & CIS.
*4 ★As of now, 45 factories have realized net zero factories.
Up to fiscal 2022: ① Panasonic Eco Technology Center Co., Ltd., ② Panasonic Energy (Wuxi) Co., Ltd., ③ Panasonic Energy (Suzhou) Co., Ltd., ④ Panasonic Manufacturing (Beijing) Co., Ltd., ⑤ Panasonic Energy (Thailand) Co., Ltd., ⑥⑦⑧ Panasonic Do Brazil (Includes 3 Factories (San Jose, Manaus, Extrema)), ⑨ Panasonic Centroamericana S.A.
Fiscal 2023: ⑩ Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd. (Sumoto Factory), ⑪ Panasonic Energy Higashiura Co., Ltd., ⑫ Panasonic Energy Nandan Co., Ltd., ⑬ Panasonic Electronic Devices (Jiangmen) Co., Ltd., ⑭ Panasonic Industrial Devices (Tianjin) Co., Ltd., ⑮ Panasonic Industrial Devices Materials (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd., ⑯ Panasonic Industrial Devices SUNX Suzhou Co., Ltd., ⑰ Panasonic Energy India Co., Ltd., ⑱ Panasonic Energy Mexico S.A. de C.V.,
Fiscal 2024: ⑲ Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd. (Motomiya), ⑳ Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd. (Suminoe Factory), ㉑ Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd. (Tokushima Factory), ㉒ Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd. (Nishikinohama Factory), ㉓ Panasonic Motor (Zhuhai) Co., Ltd., ㉔ Panasonic Motor (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd., ㉕ Panasonic Industrial Devices Taiko (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd., ㉖ Panasonic Industrial Devices (Qingdao) Co.,Ltd., ㉗ Panasonic Manufacturing (Xiamen) Co., Ltd., ㉘ Panasonic Industrial Devices Materials (Suzhou) Co., Ltd., ㉙ Panasonic Industrial Devices Materials (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., ㉚ Panasonic Industrial Devices Singapore Pte. Ltd., ㉛ Panasonic Carbon India Co., Ltd.
Fiscal 2024: ㉜ Panasonic Corporation Electric Works Company Niigata Factory, ㉝ Panasonic Corporation Electric Works Company Tsu Factory, ㉞ Panasonic Solar Amorton Co., Ltd., ㉟ Panasonic Electric Works Electrical Construction Materials Mie Co., Ltd. Headquarter Factory, ㊱ Panasonic Electric Works Electrical Construction Materials Mie Co., Ltd. Anotsudai Factory, ㊲Panasonic Lighting Devices Kumihama Co., Ltd., ㊳ Panasonic Switchgear Systems Co., Ltd., ㊴ Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd. (Wakayama Factory), ㊵ Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd. (Moriguchi Factory), ㊶ Panasonic Energy Kaizuka Co., Ltd., ㊷ Panasonic XC KADOMA, ㊸ Panasonic Manufacturing (Thailand) Co., Ltd., ㊹ Panasonic Industrial Devices Mexicana S.A. de C.V., ㊺ Panasonic Manufacturing UK Ltd.
*5 Press Release November 20, 2023
https://news.panasonic.com/global/press/en231120-2
*6 Press Release February 1, 2024
https://news.panasonic.com/jp/topics/205544
*7 Non-manufacturing sites
Activities for Increasing the Amount of Renewable Energy Use
To increase the amount of renewable energy in our business use, Panasonic Group has been actively promoting installation of renewable energy facilities in our own sites and renewable energy procurement from external suppliers.
The amount of renewable energy adopted at our sites*8 in fiscal 2025 marked 101 GWh.
Installation of renewable energy facilities has been actively encouraged in our own sites across the world in a way to suite to the regional characteristics. Particularly, photovoltaic power generation systems are recommended for installation wherever possible. Panasonic Heating & Ventilation A/C Company introduced a photovoltaic power generation system with an output capacity of 5.2 MW at the Panasonic Appliances Air-Conditioning Malaysia Sdn Bhd. (PAPAMY) factory in Malaysia. This system has the largest capacity in the Panasonic Group, with a projected annual power generation of approx. 5,900 MWh/year and CO2 emission reductions estimated at roughly 3,912 tons per year. With this development, renewable energy is estimated to account for roughly 20% of the total power consumption at PAPAMY's air-conditioning factory and offices.*9
*8 The amount from photovoltaic energy, wind power, and so on are included. The amount from heat pumps is excluded.
*9 Press release on December 30, 2024.
https://news.panasonic.com/jp/press/jn241206-1

Panasonic Connect Co., Ltd. introduced a photovoltaic power generation system based on the on-site power purchase agreement (PPA) model used by the Kobe Plant of Panasonic's Mobile Solutions Division to supplement its eco-conscious and sustainable energy use. This is the first time for Panasonic Connect to introduce photovoltaic power generation based on on-site PPA, except for its overseas sites. The projected annual power generation is approx.
811,000 MWh/year, with CO2 emission reductions estimated at roughly 400 tons per year. This will result in roughly 15% of power use at the plant being replaced with renewable energy.*10
*10 Press release on March 28, 2024.
https://news.panasonic.com/jp/topics/205628

Adoption of a Photovoltaic Power Generation System in Singapore
In Singapore, a photovoltaic power generation system with an output capacity of 1.0 megawatt-peak(MW) was adopted in Panasonic Factory Solutions Asia-Pacific (PFSAP) in September 2016. A total of 3,476 Panasonic PV module HIT® panels were installed on the rooftop of three factory buildings. At its peak, the factory's photovoltaic (PV) system is expected to power, on average, close to 20% of its entire energy consumption. Panasonic HIT® panels can generate more energy even on limited rooftop spaces due to industry's top-level efficiency. In addition, the panels are more suited to tropical climates, since they can also maintain high power generation performance even under high temperatures. The product is manufactured by Panasonic Energy Malaysia, located in Kulim Hi-tech Park in Kedah, Malaysia.
Installation of this system is based on a leasing agreement with Sunseap, the largest clean energy provider in Southeast Asia. This is the second, of such leasing agreement in Singapore, following the installation of a 2.4 MWp a photovoltaic power generation system at Panasonic Appliances Refrigeration Devices Singapore (PAPERDSG) in October 2015 also under a leasing agreement with Sunseap. The system in PFSAP is the second of such leasing arrangement between Panasonic and Sunseap.

Procurement of renewable energy from external sources has been also promoted across the globe. In Japan, at our own site, we are an electricity user, and at the same time, an electricity retailer (registration number: A0136). Since 2005, we have been supplying power to our own sites, factories, and offices. Utilizing our knowhows and experience of electricity procurement and trading that we have accumulated to date, we procure 100% renewable electricity generated from wind, etc., as well as electricity with environmental value such as those with non-fossil fuel energy certificates and credits to offset CO2 emissions from fossil fuel. This effort contributed to converting factories in Japan, China, and Southeast Asia to net zero factories. Furthermore, the photovoltaic power station with approx. 18,000 kW capacity for use at our own sites that we determined to develop in fiscal 2022 started its operations for Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd., in February 2023. In fiscal 2024, operation of power stations with a capacity of approx. 11,500 kW started for Panasonic Automotive Systems Co., Ltd., and Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd. In fiscal 2025, an additional power generation plant with a capacity of roughly 18,000 kW came into operation as a startup power supply for Panasonic Living Appliance and Solutions Company. In the same fiscal year, full scale supplies of power from an onshore wind power generation plant started for Panasonic Energy Company and Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd. As described above, we continue to contribute to expanding use of electricity from new renewable energy sources. We also started selling to Panasonic Group employees in Japan, electricity derived from practically 100% renewable energy in fiscal 2021.
For more information on Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd.'s renewable energy initiatives, click here.

In August 2019, Panasonic Group joined "RE100"*11, an international initiative that brings together companies committed to sourcing 100% renewable electricity for their global business operations. We aim to switch all the electricity used in our sites across the world to that sourced from 100% renewable energy by 2050. Progress in fiscal 2025 was 32.5%.
*11 Press release on August 30, 2019.
Panasonic Joins RE100 Aiming for Business Operations with 100% Renewable Energy
Activities for reducing energy use and CO2 emissions
To ensure implementation of reduction of the amount of energy used and CO2 emissions, it is important to visualize trend of the energy consumption of each facility in factory and the effects of the measures for specific emissions reduction. To date, we are working on CO2 reduction by adopting more than 40,000 measurement equipment systems and Factory Energy Management System (FEMS) at all of our global manufacturing sites, promoting METAGEJI (Meter and Gauge)*12, which visualizes and analyzes energy consumption. An example of factory energy-saving support service is on the following website.
Panasonic Corporation is conducting a demonstration experiment of the energy solution (Panasonic HX)*13 using hydrogen fuel cells in Kusatsu Factory, Shiga. Panasonic Manufacturing United Kingdom (PMUK) in the United Kingdom plans to start a demonstration of power supply and demand operation in 2025*14 to use 100% renewable energy for energy consumed in business activities by in-house power generation using pure hydrogen fuel cells and photovoltaic cells. For the demonstration at PMUK, in addition to the existing solar panels (372kW), 21 pure hydrogen fuel cells of 5 kW type (total output: 105 kW), and storage batteries (1 MWh) will be newly installed, and the power supply and demand operation in Cardiff, UK will be monitored according to the changes in weather and fluctuations in electrical power demand, with the aim of operation to supply necessary electricity with 100% renewable energy for the Microwave Oven manufacturing plant.
By using pure hydrogen fuel cells, we will not only reduce installation space and secure a stable power source, but also further improve energy efficiency by using heat generated during hydrogen power generation for heating and hot water supply. Through the demonstration of energy solutions at PMUK, we will develop solutions that best suit the regional characteristics and build relationships with local partners and business customers related to the hydrogen business.
*12 METAGEJI is a coined word created by the Panasonic Group which refers to visualizing energy consumption and implementing measurable reduction measures by adopting measurement instruments, such as meters and gauges.
*13 Panasonic HX
https://re100-gx.panasonic.com/
*14 Press Release (December 3, 2024)
https://news.panasonic.com/jp/press/jn241203-2

Demonstration experiment of pure hydrogen fuel cells in China
2022, Panasonic Energy (Wuxi) Co., Ltd. (PECW) in China, has been conducting a demonstration experiment of pure hydrogen fuel cells that supply electricity and heat. PECW achieved net zero CO2 emissions in fiscal 2022 through promoting energysaving, adopting photovoltaic panels, and procuring renewable energy. The pure hydrogen fuel cells to be used for a demonstration experiment this time are three types: firstly, starting with 30 kW small-scale power generation using six connected 5kw highly efficient pure hydrogen fuel (PHF) cells; secondly, 300 kW medium-scale power generation PHF cells for the mid- to long-term experiment; and thirdly, 1 MW largescale generation PHF cells for commercialization.
The pure hydrogen fuel cells are able to supply both electricity and heat, and create cooling air in summer by supplying hot water to a lithium bromide freezer. The demonstration experiment this time is to achieve zero CO2 emissions from energy saving and energy creation without procuring external renewable energy.


Reducing CO2emissions by changing the production methods
Panasonic Corporation Hikone Factory is steadily reducing CO2 emissions by changing the production methods for shaver blades. To achieve a deep shave, the shaver's outer blade has a complex and high precision shape with two different thicknesses. For manufacturing the blade, after pressing a stainless steel plate, the plate was bent by applying heat. As bending the plate without heating causes scratches, cracks, and variation in quality, bending the plate at an ambient temperature without scratches, etc., was a challenging task. However, a new bending process method at an ambient temperature is possible now thanks to our accumulated expertise in technology and experience, and a development of pressing conditions for bending the plate that took almost 2 years. With the new method, the electricity consumed for heating has been reduced , and at the same time, one process of the conventional processes in manufacturing blades was eliminated, in other words, shortened its production time.
Activities at Factories
Panasonic Energy Kaizuka Co., Ltd., which achieved net zero CO2 emission in fiscal 2025,produces lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) used in EVs. The company has been working across organizational divisions to reduce its CO2 emissions in line with Panasonic GREEN IMPACT, while improving productivity to respond to the increasing market demands for EVs in recent years. A Carbon Neutrality Promotion Committee, initiated by the Facility Management Division that manages facilities such as power generators, was jointly launched at three sites: the Panasonic Energy Suminoe Factory, Wakayama Factory, and Kaizuka Factory. This committee, whose participants include professionals in the fields of factory and production technologies, has been promoting production with minimum energy. Concretely, to reduce energy consumption in basic units by increasing product efficiency, they used scientific methods to established efficient drying conditions in the manufacturing process for electrode materials, which had been a bottleneck in improving efficiency in the production of electrode substrates, allowing the manufacturing speed to be increased. This method can be transferred to overseas factories such as in the U.S., where LIBs are produced on a large scale, and it is planned to introduce it on other sites from fiscal 2025. We also reduced the standby energy consumption of the charging and discharging devices used during testing by reviewing the operating procedures and eliminating unnecessary processes. To increase the ratio of renewable energy used inside and outside our factory premises, we have started to introduce photovoltaic power stations to our factory premises, purchasing photovoltaic electricity sourced from outside the factory through an offsite PPA. In fiscal 2025, we started to purchase wind power electricity through an offsite PPA.

Activities to provide supports for energy-saving in the China region
The long-term state policy announced by the Chinese government includes carbon peak out and carbon neutrality, focusing on further reductions to CO2 emissions. With its many business sites in China, the Panasonic Group introduced a three-year energy-saving support initiative in the country in fiscal 2023 designed to achieve efficient energy-savings across the entire region in line with China's long-term state policy. In fiscal 2025 we are lowering CO2 emissions at our model sites by carrying out energy-saving assessments in collaboration with experts from inside and outside the Group and developing human resources to introduce independence in support of energy conservation in each region. We select and actively communicate best practices gained from the energy saving diagnoses, and provide a scheme that links facility manufacturers and our sites to solve technical issues. These efforts support each site in utilizing information comprehensively for its own energy saving activities. We are also working on visualizing our energy-saving activities and how to disseminate the information effectively, improving the infrastructure for energy efficiency by installing portable measurement equipment and providing energy efficiency analysis tools, etc. In working to establish net zero factories, we continue with our rapid and low cost energy-saving measures to improve the level of energy saving in China's regions.

Fiscal 2025 Results
These efforts in fiscal 2025 resulted in 4.5 TWh*15 of the energy used in business activities, and the amount of CO2 emissions was 1.24 Mt. The fiscal 2025 investment to reduce the amount of energy used and CO2 emissions by the efforts was 3.2 billion yen.*16
*15 In fiscal 2021, the unit used to measure the energy consumed in business activities was changed from TJ to TWh. The consumed power is measured in kWh and the consumed fuel is measured using its calorific value and then converted to electrical power units at 3.6MJ/kWh. These two values are then totaled.
*16 The total amount includes all investments concerning reduction of the amount of the energy used and CO2 emissions. Note that differences or proportions of the investment are not calculated.
*17 Includes Panasonic Energy Corporation of North America since fiscal 2021.
CO2 Emission in Business Activities and CO2 Emission (by region) Per Intensity
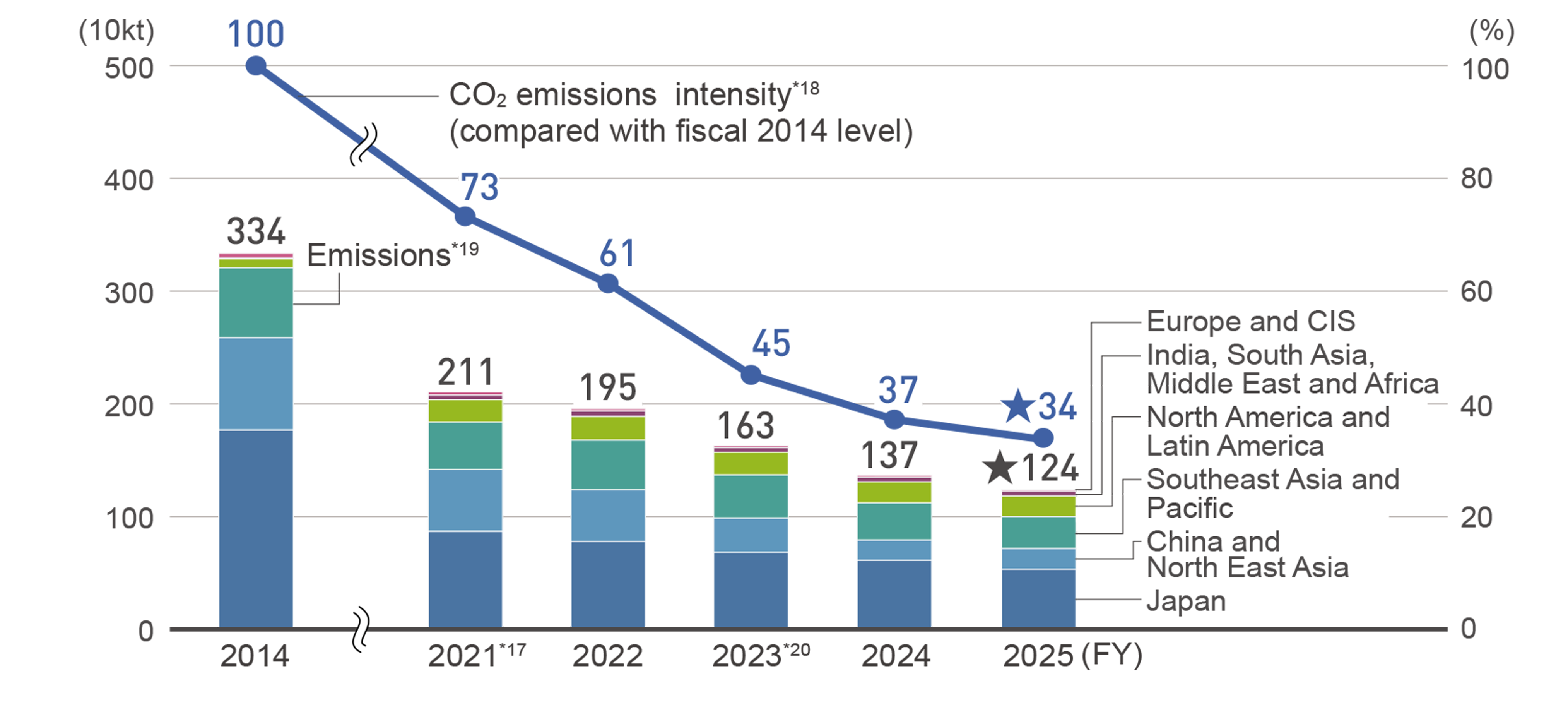
*18 We calculated the improvement rate of the 'CO2 emissions intensity' versus that of fiscal 2014', which was obtained by dividing CO2 emissions by the sales volume of all Group companies.
*19 The CO2 emission relevant to fuels was obtained by calculating with the factors stated in the "Guidelines for Calculation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions" published by Japan's Ministry of Environment. The factors for purchased electricity by country per fiscal year defined in "CO2 emissions from fuel consumption" by International Energy Agency (IEA). The FY2014 factors in the Book 2017 were used for FY2014. The FY2018-2021 factors in the Book 2019 were used for FY2018-2021. The IEA Emissions factors 2021 were used for FY2022, the IEA Emissions factors 2022 were used for FY2023, the IEA Emissions factors 2023 were used for FY2024, and the IEA Emissions factors 2024 were used for FY2025. The factors for domestically purchased electricity in Japan for fiscal 2025 stated in the "Guidelines for Calculation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions" published by Japan's Ministry of the Environment.
*20 Includes non-manufacturing sites after FY2023
Breakdown of Total GHG Emissions (CO2-equivalent) in Business Activities (by category)*21
[Unit: kt]
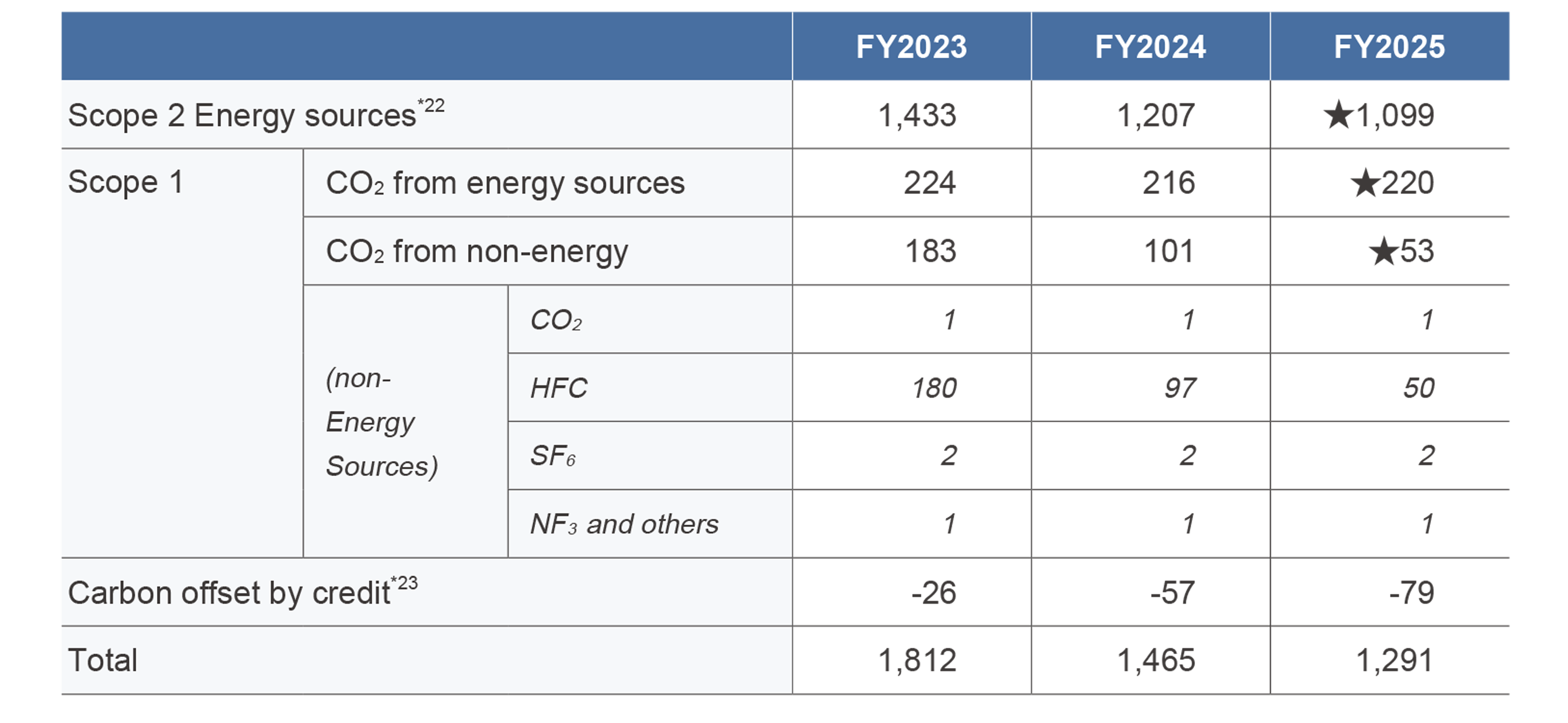
*21 The emissions of GHG other than CO2 from energy sources by Hussmann Parent Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries, Panasonic Corporation of North America, and non-manufacturing sites are not included.
*22 Electricity certificates such as Non-Fossil Certificates (NFC), International RECs (I-REC) and Green Electricity Certificates (GEC) are used.
*23 Carbon offset by credit based on the certification system such as J-Credits, Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), and Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) are used.



